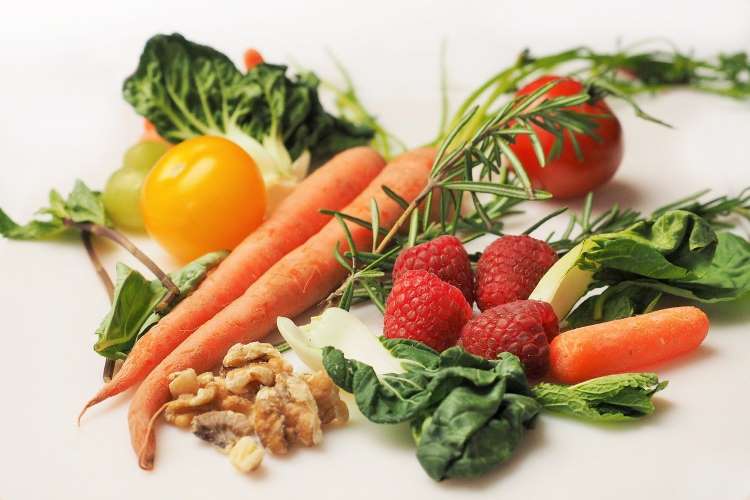
Roughage is also known as dietary fibre. It’s the part of a plant’s food that can’t be digested. They do not supply any nutrients to our bodies, but they are an important part of a balanced diet. Roughage is a carbohydrate and humans cannot digest them in the small intestine, it gets absorbed in the large intestine.
Learning courses for your kids! Get free trial here
What is roughage?
Roughage is commonly known by one name. Do you know what the other name of roughage is? It is commonly known as dietary fibre or bulk. So if we don’t consume food rich in roughage, our digestion and health can suffer. Better the fibre, the better the digestion will take. Roughage is found naturally in plants. Grains, fruits, vegetables and legumes like beans and peas are all good sources of dietary fibre. Roughage is classified into two types based on solubility – soluble and insoluble fibres.
Learning courses for your kids! Get free trial here
1. Soluble fibres
When soluble fibre enters the stomach and intestines, it dissolves in water and gastrointestinal fluids. It turns into a gel-like substance that is digested by bacteria in the large intestine, releasing gases and a few calories in the process. One of the most important functions of soluble fibre is to reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. It also helps in controlling blood sugar level. Soluble fibre is found in food items like fruits, beans, nuts, citrus fruits, berries etc.
2. Insoluble fibres
Insoluble fibre, in contrast to soluble fibre, does not dissolve in water. Dietary fibres that do not pull in or swell up in water to produce a gel-like substance are known as insoluble fibres. Insoluble fibre, on the other hand, travels right through our digestive system, bulking up our stools. Insoluble fibre, because of this property, may aid in the prevention of a variety of stomach-related problems, such as constipation. Whole grains, beans, nuts, and some vegetables have the largest levels of insoluble fibre. In addition, resistant starch also gives the effect of roughage.
3. Resistant starch
Starch that is resistant to attack. While resistant starch isn’t generally thought of as fibre, it has a comparable effect. The portion of starchy food (about10%) that resists regular digestion in the small intestine is known as resistant starch. Many unprocessed bowls of cereal and grains, as well as unripe bananas, potatoes, and lentils, contain it, and Hi-Maize is used to add it to bread and morning cereals. Cooking and manufacturing procedures such as snap freezing can also be used to create intestinal health, resistant starch is crucial. Bacteria in the large intestine ferment the resistant starch and convert it to short-chain fatty acids, which are beneficial to bowel health and may help prevent cancer.
Also read: Benefits of Surya Namaskar For Kids: Yoga for the Perfect Balance of Healthy Mind and Body
What is the importance of roughage in our diet?
What is the role of roughage in our body? The function of roughage is not only to help us to stay regular. We should eat more roughage because many studies have shown that eating high fibre improves our immune system and overall health, also the way we look and feel. So let find out what is the role of roughage in our body.
1. Digestive health
Digestive health is important. By thickening up stools and making them easier to pass, roughage helps in normalising bowel movements. Health issues related to digestion like diarrhoea and constipation can be relieved and prevented by roughage. Diverticulitis (intestinal inflammation), kidney stone, haemorrhoids, gallstones, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can all be reduced by eating a high-fiber diet. A high-fiber diet has also been shown in certain studies that help in minimising the risk of GERD and ulcers in lowering gastric acid.
2. Cancer
Although the evidence is not yet explicit, some study suggests that eating a high-fiber diet can help prevent colorectal cancer to a great extent. High-fiber diets have also been related to a reduced incidence of other common digestive system malignancies, such as stomach, mouth, and throat cancers.
3. Skin health
Yeast and fungus can cause acne breakouts when they are concealed through the skin. Fiber, particularly psyllium husk (a type of plant seed), oat bran and apple skin can help eliminate toxins from our body, enriching our appearance and skin health. Skin-care miracloccururs by adding roughage in our diet. Fibre promotes blood circulation, maintains it thin, and increases the progression of nutrients and oxygen to skin cells, boosting the appearance of our skin from the inside out.
4. Heart health
Fiber, especially soluble fibre, is an essential component of any heart-healthy diet. By lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol, a high-fiber diet can help to lower cholesterol levels. A high fibre diet can also help you prevent metabolic syndrome, which is a collection of risk elements connected to coronary heart disease, stroke and diabetes. Roughage can also aid in the reduction of blood pressure, the increase of HDL (good) cholesterol and inflammation, as well as the loss of abdominal fat.
5. Weight loss
Roughage adds bulk to our diet, which is important for both losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight. It also cares for digestion and prevents constipation. Roughage might make us feel fuller rapidly. Because fibre lingers in the stomach longer than other foods, we’ll feel fuller for longer, which will help you eat less. Because high-fibre foods like fruits and vegetables are low in calories, putting in roughage to our diet makes it simpler to lose weight high fibre diet can also help you lose weight in other ways:
- It can help preserve our body’s fat-burning capability and minimise insulin spikes that make us feeling fatigued and seeking unhealthy meals by controlling our blood sugar levels.
- Roughage can help move fat through your digestive system more quickly, allowing less of it to be absorbed.
- When we consume high-fiber foods like fruit, we will have more energy to exercise.
Also read: Muscular Strength Exercises for Kids: Benefits and Techniques to Master for a Healthy Body
Learning courses for your kids! Get free trial here
Which food item has roughage?
So far we have discussed the function of roughage and what is the importance of roughage in our diet. Most of you have wondered which food item has roughage. Here are some foods high in fibre that we should eat on a regular basis.
1. Vegetables
Vegetables are known for their high mineral and vitamin content, but some vegetables, such as cucumber, zucchini, sweet potato, and broccoli, also have a high fibre level. Green leafy vegetables are high in insoluble fibre, which works as a laxative in the remedy of IBS and constipation. Dark coloured vegetables are rich in fibre, The fibre content of collard greens and Swiss chard is 4 grams per cup. Artichokes are high in fibre, with a medium-sized one containing 10 grams.
2. Whole grains
Focusing on whole grains is one of the simplest strategies to increase roughage consumption. In nature, grain is the complete seed of a plant, including the bran, germ, and endosperm. Refining the grain removes the germ and bran, resulting in the loss of protein, fibre, and other essential components.
If you haven’t done so before, it’s time to make the move to whole grains. Slowly introduce whole grains to your digestive system, increasing your daily portions as you go. Dietary fibre is abundant in whole grains such as oatmeal, oat bran, brown rice, granola, quinoa, and whole-grain wheat. Switching to whole grains does not mean that you should completely avoid white bread in your diet, but it is recommended that you include more whole grains in your diet.
Learning courses for your kids! Get free trial here
3. Fruits
Fruits, like vegetables, have a high content of vital vitamins and minerals, as well as roughage. Soluble fibre is found in most fruits and helps lower cholesterol levels in the blood. Roughage is abundant in citrus fruits and other fruits with edible peels. Dragon fruit is an example of a fibre-rich, healthy fruit. Some other fruits rich in fibre are avocado, strawberry, guavas, raspberries, pomegranate etc.
4. Legumes
The best source of insoluble fibre for our body is legumes. Leguminous foods include lima beans, lentils, kidney beans and black beans. Cooked kidney beans have up to 8 grams of roughage in a single serving. They’re also nutrient-dense, thanks to the potassium, zinc, and iron they contain. Legumes are also a good source of protein.
5. Nuts
Walnuts, almonds, and peanuts, for example, are excellent sources of roughage. They’re also high in calories, making them an excellent complement to a weight-loss regimen. The digestible omega three fatty acids found in nuts are crucial because they raise good cholesterol levels in the blood while also boosting roughage content.
Also read: How are Exercise and Yoga Helpful for Your Child’s Health: Guide to a Healthy Life
Conclusion
We are all given the option of living a healthy lifestyle or not. This decision is reflected in our nutrition, and what we eat has a profound impact on our bodies and lives. While it is beneficial to include roughage in your diet, it is also crucial to realise that a high roughage content might be risky. Nutritionists recommend that you consume at least 21 to 38 grams of fibre each day, depending on our age and gender. Make a diet that meets all of your nutritional and roughage requirements.